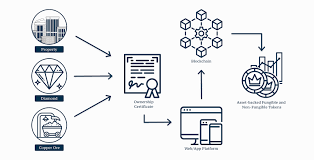
Tokenization is emerging as a critical link between traditional financial systems and blockchain infrastructure, enabling real-world assets to be represented, traded, and managed more efficiently in digital form.
For decades, traditional finance has relied on centralized intermediaries, manual processes, and fragmented infrastructure to manage assets such as real estate, equities, bonds, and commodities. While effective at scale, these systems are often slow, costly, and inaccessible to a global audience. Blockchain technology introduces a fundamentally different approach — and tokenization sits at the center of this transformation.
What Is Tokenization in Finance?
Tokenization refers to the process of converting ownership rights of real-world or financial assets into digital tokens recorded on a blockchain. These tokens represent a verifiable claim on an underlying asset and can be transferred, settled, or divided with far greater efficiency than traditional instruments.
In financial contexts, asset tokenization can apply to:
- Real estate and property shares
- Equities and private company shares
- Bonds and debt instruments
- Commodities such as gold
- Funds and structured products
By using blockchain as the settlement layer, tokenized assets benefit from transparency, programmability, and near-instant transferability.
Why Traditional Finance Is Adopting Tokenization
The growing interest from banks, asset managers, and financial institutions is driven by tangible operational advantages rather than speculation.
Key benefits include:
- Improved liquidity: Illiquid assets can be fractionalized, enabling broader participation
- Faster settlement: Blockchain reduces settlement times from days to minutes
- Lower costs: Fewer intermediaries and automated processes reduce overhead
- Global accessibility: Assets can be accessed and transferred across borders more easily
Major institutions have already begun exploring tokenized bonds, funds, and money-market instruments as a way to modernize legacy infrastructure without fully abandoning existing regulatory frameworks.
Tokenization as a Bridge, Not a Replacement
Importantly, tokenization does not aim to dismantle traditional finance overnight. Instead, it acts as a bridge between established financial systems and blockchain-based infrastructure.
In many cases:
- Assets remain legally recognized within existing frameworks
- Custodians and compliance processes still play a role
- Blockchain is used as a settlement and record-keeping layer
This hybrid approach allows institutions to experiment with blockchain benefits while maintaining regulatory compliance and investor protections.
The Role of Smart Contracts and Infrastructure
Smart contracts are a key enabler of tokenized finance. They allow rules around ownership, transfers, dividends, or compliance checks to be encoded directly into digital assets.
Combined with emerging blockchain infrastructure — including scalable networks and regulated custody solutions — tokenization becomes practical for large-scale financial use cases rather than niche experimentation.
For readers seeking a deeper, structured explanation of how asset tokenization works in practice and why it matters for modern finance, this guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of the concept and its real-world implications.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential, tokenization still faces challenges:
- Regulatory clarity varies by jurisdiction
- Interoperability between platforms remains limited
- Standardization is still evolving
However, ongoing collaboration between regulators, financial institutions, and blockchain developers suggests these obstacles are gradually being addressed.
Looking Ahead
As financial markets continue to digitize, tokenization is likely to play an increasingly central role in how assets are issued, managed, and traded. By combining the trust and scale of traditional finance with the efficiency and transparency of blockchain technology, tokenization represents a practical path toward a more accessible and modern financial system.
Rather than a disruptive replacement, it is shaping up to be the connective layer that allows both worlds to evolve together.