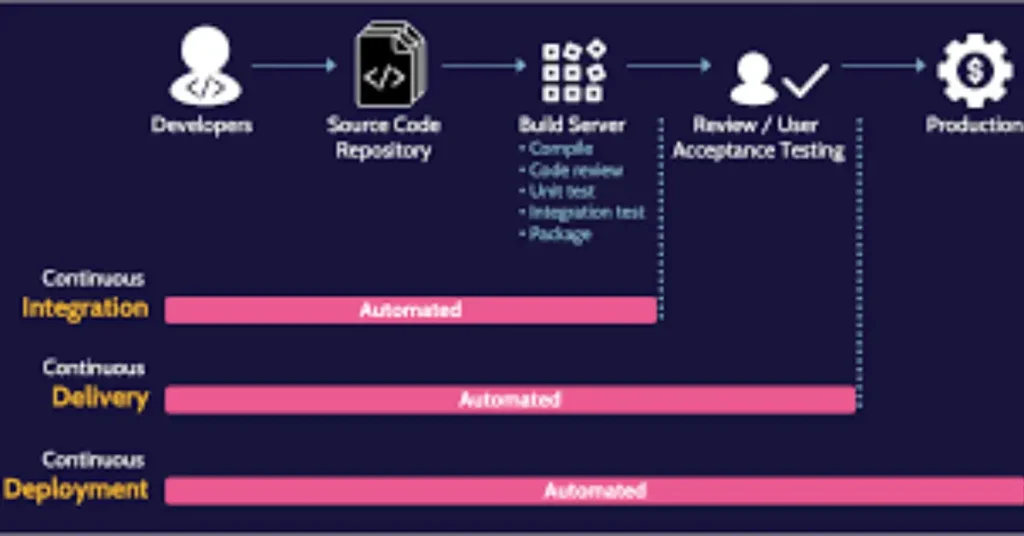
With threats and vulnerabilities ever changing, information security is a major worry in the digital world of the present. Construction of robust systems requires a thorough grasp of fundamental security ideas. In this handbook, they examine the essential components of efficient information security, emphasizing the underlying ideas that create a strong security architecture.
Building Sturdy Security Systems
Organizations need to consider plenty of factors whilst growing stable structures. These include detecting vulnerabilities, taking protective measures, and growing steady communication routes. Robust security requires the integration of numerous technical and administrative controls throughout the layout method.
Installing Secure Infrastructure
All effective safety plans are constructed on a strong infrastructure. This requires putting in stable networks, securing servers, and making sure that bodily additives are nicely blanketed. The appropriate software for these factors can substantially lower the chance of unwanted access and records loss.
Controlling User Authentication and Access
Controlling who may additionally get entry to data is a critical part of safety. It involves not only technology but also sturdy regulations and methods. Organizations ought to use numerous strategies to authenticate users and guarantee that the best legal employees may also access touchy information. This incorporates multi-thing authentication and secure identification verification mechanisms.
Protecting Sensitive Information
Organizations create and analyze huge volumes of sensitive information, and guaranteeing its protection is vital. This incorporates enforcing encryption, creating secure statistics garage mechanisms, and putting guidelines for data management. Protection doesn’t stop with information storage; it extends to how records are transported and shared.
Preparing for and Responding to Security Incidents
Even with effective preventive efforts, safety events can occur. Organizations want to be prepared with efficient reaction strategies. This entails recognizing issues fast, assessing their effect, and taking movements to lessen damage. Denial-of-service assaults and statistics breaches are the handiest two examples of the many conditions that response teams want to be organized for.
Meeting Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Law and regulatory adherence is equally as crucial to information protection as technology. Businesses want to be aware of their criminal duties regarding records management, privacy, and facts safety. This implies that to stay out of criminal hot water and preserve public self-assurance, one ought to live cutting-edge with pertinent legal guidelines and enterprise norms.
Encouraging a Culture Aware of Security
The individuals putting a security plan into exercise make it stronger or weaker. Organizations must foster a lifestyle of security focus in which personnel participants are aware of their component in statistics safety. This requires constant schooling, unambiguous policy verbal exchange, and promotion of first-class practices in any respect organizational ranges.
Security Domain Interconnection
cissp eight domains names are related even if they each have a wonderful consciousness. All of those additives are covered in an intensive protection plan to guarantee that they cooperate to guard the property of the company. Whole device compromise would possibly result from a single hollow, for this reason, holistic thinking is critical.
Continuous Development and Flexibility
New risks are continually appearing inside the dynamic realm of information safety. Organizations want to be bendy, always assessing and enhancing their protection approaches. This calls for constant technology and coverage evaluation, testing, and upgrading. Businesses might also keep ahead of possible threats and preserve a sturdy safety posture by adopting an attitude of ongoing development.
Setting Security and Usability in Balance
A problem in information security is striking the ideal balance between user ease and security measures. Though tight restrictions are generally necessary for robust security, too rigorous systems can reduce productivity and encourage users to look for workarounds. Enterprises need to create security procedures that safeguard data without impeding creativity or making operations more difficult.
The Part Emerging Technologies Play
Information security is shaped in large part by emerging technology. More and more, security is being improved by using developments like blockchain, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. Greater transparency in safe transactions, automation of monotonous security chores, and threat detection may all be achieved with these technologies. They also pose fresh threats, though, so businesses need to be aware of and prepared for them.
The Value of Drilling and Incident Simulation
A solid security posture is mostly determined by preparation. Organizations should routinely practice and simulate to react to occurrences successfully. Teams can rehearse their duties in a controlled setting and incident response plans are tested by these exercises. Organizations may improve their preparedness for actual security incidents by pointing holes and improving processes.
Partnership and Information Exchange
The attempt to secure information is group work. Better able to defend themselves are organizations that cooperate and exchange knowledge about risks and weaknesses. Collaboration amongst industry associations, government agencies, and commercial enterprises is common to exchange information and create the best procedures. An enhanced robustness and resilience of the security ecosystem might result from this cooperative strategy.
Controlling Risks From Third Parties
For everything from software development to cloud storage, many companies depend on outside suppliers. These alliances bring new dangers even if they might be advantageous. Organizations must set up precise expectations for data protection and carry out comprehensive evaluations of the security procedures of their suppliers. Effective risk management of third parties helps companies to prevent vulnerabilities coming from outside sources.
A Growing Danger from Social Engineering
Targeting human behavior to get past security measures, social engineering assaults are becoming more common. These assaults make use of psychology and trust to get illegal access or retrieve private data. Attackers frequently employ baiting, pretexting, and phishing. Workers in organizations need to be made aware of these hazards and measures taken to identify and stop social engineering attempts.
The Integration of Security into Business Strategy
To be effective, security has to be included in the whole company plan. This is making sure that leadership recognizes the need for strong security procedures and matching security objectives with corporate goals. Security may be made a shared responsibility in a company by integrating security into decision-making and business operations.
Conclusion
It takes constant effort to comprehend and put into practice the several facets of information security. From technological measures to psychological aspects, the eight domains of cissp include a broad spectrum of ideas that all add to a complete security plan. Organizations that want to succeed need to take a comprehensive stance, always adjust to new threats, and promote a culture of security awareness.
Companies may create a robust security architecture by concentrating on these ideas and staying dedicated to ongoing development. With this strategy, they are not only safe from present dangers but also well-positioned to take on new ones.