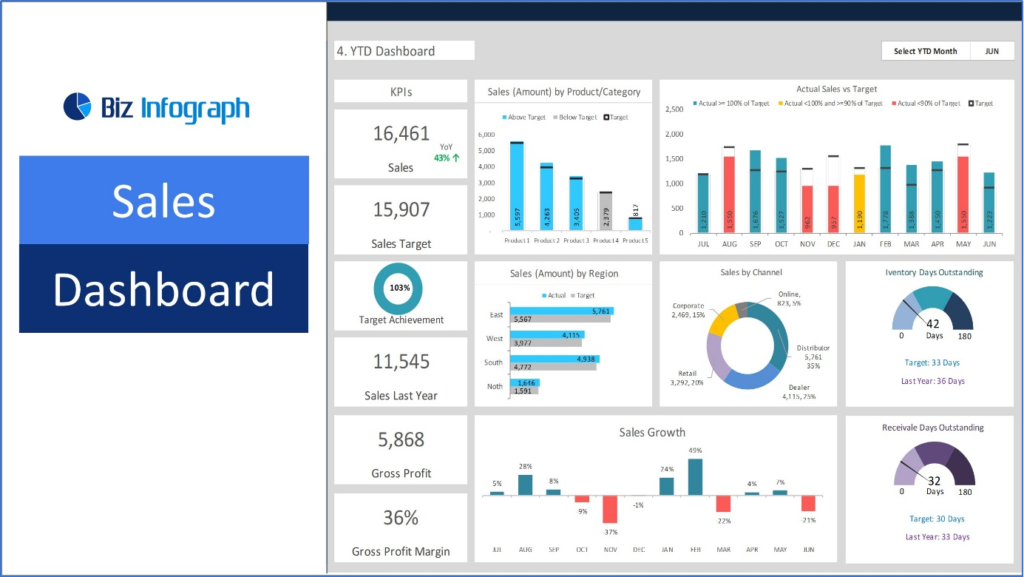
Introduction to a sales dashboard
A sales dashboard is a management tool that gives an actual picture of various aspects of sales and its key activity measures. It aggregates information on sales activities, goals, and results into simple charts and graphics that allow for a fast and clear understanding of further actions, decisions, and strategies. Sales Dashboard: Track performance, optimize strategies, and boost revenue effectively and efficiently.
What is a sales dashboard?
A sales dashboard is generally a graphical user interface that displays information about sales. It contains graphs, numbers, and charts that provide the sales team with figures on current performance and the organization’s activities.
There are many standard sales dashboard measurements, such as closed business ($), sales velocity, lead-to-business ratio, pipeline data, and sales and rep activity. Sales dashboards report real-time data so that changes will reflect every new record added by a sales rep in the CRM.
Importance of Sales Dashboards in Modern Business
First, sales managers utilize the Sales Dashboard to manage their employees’ performance, submit check figures to the executives, view KPI data, and receive information on the general condition of the sales department. Some individuals employ them as monitoring tools to assess individual performance, organize work, and track personal achievements of the assigned sales goals.
There are two scenarios with dashboard reporting: The reporting function can be part of a CRM or an independent product compatible with a CRM. Occasionally, businesses will apply an integration solution with native gauges (for example, where marketing, sales, and customer success statistics must be displayed simultaneously).
Critical Components of a Sales Dashboard
Overview of Common Metrics Tracked
A sales dashboard is ordinarily used to monitor various data, including total sales, the number of sales made, sales ratios, and the state of the sales funnel. Such measures help comprehend current sales statuses, trends, and issues that require attention.
Visual Elements and Their Functions
In revenue comparisons, a bar chart is used, while a line graph is used for sales trends. A gauge displays a pie chart of market share and performance against target aspects. These visuals aid the fast evaluation of data, operation of a pattern, and detection of an outlier.
Customization Options to Fit Your Business Needs
They can, hence, be configured by prioritizing the business’s critical performance indicators. The available features include flexible settings, which can be applied depending on time, geographical location, or the specific team’s sales, as well as integration with other tools like customer relations management systems. This makes it easy for the dashboard to incorporate the sales tactics specific to your business and operational style.
Setting Up Your First Sales Dashboard
Selecting the Right Dashboard Software
When selecting dashboard software, the solution should meet the organization’s requirements and be compatible with other applications. As the criteria, one may employ elements that are superior in form, including simplicity, expandability, and adjustability in terms of the reports created. Some trending tools include Salesforce Analytics, Tableau, and MS Power BI.
Integrating Sales Data Sources
Your dashboard should be able to extract data from other sources like CRM and systems, marketing spreadsheets, and various other marketing platforms. It affords a 360-degree perception of sales performance and dessertsa the creation of data silos that obstruct proper analysis of the sales force performance figures.
Tips for Effective Dashboard Layout
Utilize formats that are easy to understand and have proper identification and categorization. The critical data can only be highlighted without cluttering the dashboard so that users can make a quick decision based on a straightforward interpretation of the data presented.
How to Read and Interpret Dashboard Data
Understanding Data Visualizations (Graphs, Charts, Indicators)
Even when using a sales dashboard, it’s critical to understand how each display type works and the relevant data model. Graphs, which include bar and line charts, are used for trends and comparisons over time. Pie charts are used for proportions and market share, while gauges or indicators estimate achievements. All of them have specific uses, and they aim to make the complexity of the data and achievements more comprehensible.
Analyzing Sales Trends and Patterns
Search for repeated increases or decreases in sales indicators, variability in performance, and relations between the different parameters. For instance, a gradual incline in the sale rate of certain products in an area points to successful strategies or conditions in the market. These patterns make a valuable contribution in terms of gearing future expectations of performance and the causes that drove sales.
Utilizing Data to Make Informed Decisions
Immerse yourself in the findings acquired from analyzing the trends to make a triumphant-driven decision. For instance, if the converted rate is high in the specific sales team, then there are grounds to adopt the strategies used by the group and other teams. Kindly apply the data to review the sales strategies to maintain change over the resource partitioning and targets. Daily or weekly analyses and interpretations of the data represented on dashboards help make decisions by utilizing updated information to improve the performance of business processes.
Best Practices for Maintaining Your Sales Dashboard
Regular Updates and Revisions
Make sure to update your sales dashboard frequently to have updated numbers and percentages. Optimize KPIs and levels of measures, incorporate new data, and update visualizations according to business changes. This keeps the information on the dashboard current for constant analysis to support the organization’s decision-making.
Training Your Team to Use the Dashboard Effectively
Ensure that you formally train your team on the dashboard, including how and where to find the data being shown in the dashboard. One can target core features, that is, learn how to use filters or interpret various graphics. This is a wise measure to take to ensure those proficient in reading reports are included in the loop while allowing others on the team to get the maximum out of the dashboard and data in general.
Security Measures to Protect Your Data
Apply strict security measures to keep your dashboard data secure. Implement role-based access controls that ensure information is accessible only to eligible users. Periodically change passwords and ensure they are not compromised. Accomplishing data security eliminates the vulnerability your business is most likely to experience, safeguarding your sales data.
Leveraging Your Dashboard for Sales Growth
Identifying Opportunities for Upselling and Cross-Selling
Customers’ purchasing patterns and frequency should be checked on the dashboard. Seek evidence that the organization has the potential to sell more of the product or to sell related products. For instance, assume that one of your customers is a repeat purchaser of related goods; the next time they visit the store, they should be able to receive promotions or specially packaged offers. It may lead to further sales and improvement of client interactions, increasing the likelihood of increased income by targeting notable interest clients.
Spotting and Addressing Sales Declines Promptly
Keeping an eye on your sales, significantly your monthly, weekly, or daily sales, will help you identify early signs of a drop in sales or your low-performing region. Look for onsets of decline or continuously down-spiraling statistics. Determine the cause, including shifts in market conditions or problems in the sales process, and respond by planning immediate corrective measures.
Forecasting Sales and Setting Realistic Goals
You can easily predict future sales by using the data accumulated from your history and current tendencies in the sales forecast tools. Utilize the information to develop reasonable goals and correlate your sales plan with the expectations. It directs the resources and plans for the business, enhancing sales growth and performance in the long run since forecasts are a reliable means of averting risks.
Advanced Tips and Tricks for Power Users
Integrating External Tools and APIs
Expand the capabilities of your dashboard by using various imports from outside of web delivery, such as CRM, marketing or other analytical tools, and APIs. The integration saves time because it eliminates the need for data transfers across different applications and offers a broad perspective of sales performance, thus collecting all essential details in one location.
Automating Reports and Alerts
Whenever metrics and changes occur, automatically created reports or alerts are received. This automation reduces the time it takes to respond to new trends or any incidence that is worth notifying the public.
Personalizing Dashboards for Different Team Roles
Configure the dashboards according to the target personnel to show only the information that a particular function is interested in. This improvement of use enhances efficiency and guarantees that everyone on the team receives information relevant to the tasks assigned.
Conclusion
The Biz Infograph dashboards mainly provide an uncluttered look and easy access to the most crucial sales figures, which help in constantly monitoring, analyzing, and deciding. They assist a business in terms of recognizing trends, channeling sales strategies, and attaining the laid-down objectives, especially in the most efficient manner.
Always investigate how to use the features on the sales dashboard. Daily interactions with the functions can reveal more sophisticated features and possibilities related to data enhancement and business adjustments to achieve steady sales and operational effectiveness.