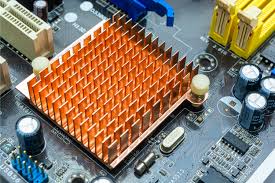
Electronic devices naturally generate heat, and managing it is essential for performance and longevity. Whether it’s a laptop, gaming console, or smartphone, overheating can cause problems. Passive heat sinks help by dissipating heat without fans or moving parts, making them a simple and reliable cooling solution.
In this post, we’ll explore how they work, their benefits, different types, and what to consider when choosing one. Let’s dive in and discover how to keep your devices cool!
What is Heat Dissipation and Why is it Important?
Heat dissipation is transferring heat away from a device or component to maintain safe operating temperatures. As electronic devices function, they generate heat due to electrical resistance and energy loss. Without proper heat management, overheating can occur, leading to performance degradation or even hardware failure.
Why is Heat Dissipation important?
- Prevents Overheating – Excessive heat can cause thermal throttling, reducing performance to protect components.
- Enhances Reliability – Keeping temperatures in check helps prolong the lifespan of electronic devices.
- Maintains Efficiency – Proper cooling ensures consistent performance, particularly in high-power applications like computing, telecommunications, and industrial automation.
- Supports Safety & Innovation – Heat management ensures stability and innovation in electronics.
Effective heat dissipation is crucial for efficiency, reliability, and safety in modern technology.
Understanding the Basics of Passive Heat Sinks
Passive heat sinks play a crucial role in thermal management by dissipating excess heat without relying on external power or fans. Instead, they utilize natural convection to regulate temperatures efficiently.
How Do Passive Heat Sinks Work?
- Constructed from high thermal conductivity materials like aluminum or copper, they transfer heat away from sensitive components.
- Designed with fins or ridges to maximize surface area, allowing for greater airflow and heat dissipation.
- Unlike active cooling solutions that use moving parts, passive heat sinks operate silently and require no maintenance.
Why Choose a Passive Heat Sink?
- Reliable & Maintenance-Free – No fans or pumps to fail over time.
- Energy-Efficient – Operates without electricity, making it eco-friendly.
- Ideal for Compact & Quiet Applications – Suitable for electronics where space is limited and noise reduction is a priority.
Understanding these fundamentals provides a solid foundation for exploring specific types of passive heat sinks and their unique applications in various industries.
Types of Passive Heat Sinks
Passive heat sinks come in various designs, each optimized for specific applications. Choosing the right type depends on thermal requirements, space constraints, and material considerations.
1. Finned Heat Sinks
Finned heat sinks are designed with extended surfaces (fins) to maximize heat dissipation. By increasing surface area, they enhance airflow and improve cooling efficiency. These heat sinks are ideal for applications where natural convection plays a significant role, such as CPUs and power amplifiers. Their adaptability makes them suitable for small and large systems, ensuring reliable thermal management.
2. Extruded Heat Sinks
Extruded heat sinks are manufactured by pushing heated metal, typically aluminum, through a die to form precise, intricate profiles. This process allows for high thermal conductivity and lightweight yet durable construction. Their customizable design makes them a versatile choice for applications ranging from electronics to automotive systems, offering efficient cooling with minimal complexity.
3. Stamped Heat Sinks
Stamped heat sinks are created by stamping metal sheets into specific shapes, providing a cost-effective cooling solution. Commonly made from aluminum, these heat sinks offer an increased surface area for better airflow. Their affordability and ease of customization make them ideal for industries like electronics and automotive, where space efficiency and reliable cooling are essential.
4. Bonded Fin Heat Sinks
Bonded fin heat sinks use advanced bonding techniques to attach fins to a base, significantly increasing the surface area for heat dissipation. This design ensures excellent thermal conductivity and structural integrity, making them more effective than conventional designs. Their lightweight and customizable nature makes them suitable for high-performance applications like processors and LED lighting.
Each type of heat sink has its advantages, with selection depending on factors like space constraints, cooling needs, and cost considerations
How Do Passive Heat Sinks Work?
Passive heat sinks function using thermal conduction and natural convection to dissipate heat without relying on fans or other moving parts.
- Thermal Conduction: When an electronic component (e.g., CPU or LED) generates heat, the attached heat sink absorbs it. Materials like aluminum or copper, known for their high thermal conductivity, quickly transfer this heat away from the source.
- Natural Convection: As the heat sink absorbs heat, the surrounding air warms up and rises because hot air is lighter. Cooler air then moves in to take its place, creating a natural airflow cycle. This continuous process helps remove heat without needing fans or other external cooling.
Passive heat sinks use finned designs to maximize surface area, enhancing heat dissipation for stable performance and longer device lifespan.
3. Thermal Conductivity vs. Thermal Resistance
- Thermal Conductivity: Measures how well a material transfers heat. Higher values (e.g., copper > aluminum) mean faster heat dissipation.
- Thermal Resistance: Represents a material’s opposition to heat flow. Lower resistance = better cooling efficiency.
Balancing these properties ensures optimal passive cooling for electronics, preventing overheating and improving reliability.
4. Natural vs. Forced Convection
- Natural Convection: Relies on rising warm air and cooler air moving in to replace it. It’s silent, maintenance-free, and ideal for low-power applications.
- Forced Convection: Uses fans or pumps to actively move air over surfaces, significantly improving cooling performance but requiring energy and additional components.
Passive heat sinks excel in well-ventilated environments where silent, energy-efficient cooling is preferred.
Benefits of Using a Passive Heat Sink
Passive heat sinks offer several advantages, making them a preferred choice in many applications. Their reliability, cost-effectiveness, and silent operation set them apart from active cooling solutions.
1. Increased Reliability
Passive heat sinks improve reliability by removing excess heat without needing electricity or moving parts. Since they have no mechanical components, there’s less chance of failure, which means fewer repairs and lower maintenance costs. Passive heat sinks enhance device reliability by efficiently dissipating heat, extending component lifespan, and maintaining performance across various applications. Their simple design makes them durable and dependable, especially for important systems that must always function properly.
2. Cost Effectiveness
Passive heat sinks are cost-effective as they use natural convection, eliminating the need for power and complex systems. Their simple design lowers manufacturing, installation, and maintenance costs while ensuring a longer lifespan than active cooling solutions. With no energy consumption, they reduce operating expenses over time. Businesses can optimize thermal management efficiently, saving money while maintaining performance.
3. Low Noise Operation
Passive heat sinks work silently because they don’t use fans—they rely on natural airflow to cool devices. This makes them ideal for quiet environments like homes and offices, where there’s no distracting humming or whirring. They also save energy since they don’t need power-hungry cooling systems. Industries like healthcare and audio equipment benefit from this noise-free design, ensuring efficiency and user comfort.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Passive Heat Sink
Passive heat sinks play an important role in managing heat dissipation without the need for active cooling components like fans. Choosing the right heat sink involves considering several factors to ensure optimal thermal performance and longevity.
- Thermal Requirements – Determine the heat dissipation needed and select a heat sink that meets those demands.
- Material Choice – Aluminum is lightweight and cost-effective, while copper provides better thermal performance at a higher price.
- Size & Shape – Ensure it fits your design without blocking airflow; finned designs improve cooling efficiency.
- Airflow Considerations – Allow space for natural convection to enhance heat dissipation.
- Environmental Factors – Consider dust, moisture, and potential corrosion; anodized coatings can improve durability.
By carefully evaluating these aspects you can select a passive heat sink that ensures efficient cooling, reliability, and longevity.